 |
 |
- Search
| J Neurosonol Neuroimag > Volume 11(2); 2019 > Article |
|
Abstract
Imaging of the carotid artery wall is the focus of several ongoing research studies that are investigating the optimal approach to identify so-called “vulnerable plaques”. Even when standard arterial luminal imaging fails to indicate a stenosis in stroke patients, a non-stenotic plaque may be responsible for the stroke. Indeed, over the past decade there has been a paradigm shift in the diagnosis and risk stratification of patients with carotid artery disease, whereby nowadays more emphasis is put on plaque characterization, mainly by using computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance (MR), in addition to the usual assessment of stenosis and surface irregularities. In this review, we will discuss current state-of-the-art CT and MR techniques to characterize vulnerable plaques and summarize current developments in imaging-based assessment of carotid plaques, in order to identify ideal candidates for revascularization and to monitor the effects of medical therapy.
Stroke is the second most common cause of death worldwide and a significant proportion of all ischemic strokes are due to carotid atherosclerotic disease.1 Carotid atherosclerosis has a high prevalence in Western countries, affecting up to 75% of men and 62% of women aged 65 years and older.2
Currently, and over the last several decades, the reduction in luminal diameter of the extracranial carotid arteries has been considered to be the key parameter for stratifying the severity of carotid artery atherosclerosis. This resulted from the study design of clinical trials conducted during the 1980s to the mid-1990s.3,4 Despite these very important clinical trials, histopathological studies demonstrate that plaques with identical degrees of stenosis can display considerable differences in composition and also in risk of rupture.5
The evolution of computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance (MR) imaging techniques has allowed for the routine characterization of carotid plaque features (Figs. 1 and 2). The traditional concept of using the degree of luminal stenosis as the sole imaging marker for the selection of the optimal therapeutic approach is challenged by a rapidly growing body of literature demonstrating that plaques causing only mild stenosis may still lead to stroke.6,7 Moreover, it is important to underline that plaque composition may change dramatically over a few years and cardiovascular risk factors play a major role in these changes.8 Physicians treating patients with carotid disease should be aware of this paradigm shift since nowadays the imaging of vulnerable plaques and their characterization plays a key role towards the improvement of risk stratification and therapy selection in patients with both high- and low-degree carotid artery stenosis.
The characterization of the carotid artery atherosclerotic wall is the focus of several ongoing research efforts which investigate the optimal approach to the imaging of the vulnerable plaque.9,10 The target of plaque imaging is to look beyond the lumen using advanced wall imaging methods in order to identify the vulnerable plaque.7,11 This is a rapidly evolving field because of the evolution of CT and MR technologies that can provide exquisite, high-resolution imaging of the carotid artery lumen and arterial plaques. Literature5,12 shows that certain plaque features are associated with an increased risk of plaque rupture, including intra-plaque hemorrhage (IPH), thin or ruptured fibrous cap (FC), presence and size of the lipid-rich-necrotic-core (LRNC), and active plaque inflammation. In the following sections the features linked to plaque vulnerability are presented.
CT is a non-invasive and widely used technique that allows assessment of the atherosclerotic plaque burden and the degree of stenosis.13-17 Modern CT scanners are able to perform detailed imaging of the carotid artery lumen and of the plaque. Visualization of the vessel lumen is achieved by performing a CTA which requires the injection of an iodinated contrast medium. Because of its excellent spatial resolution, CT imaging is a promising tool for the quantification of the volume of the carotid plaque and its sub-components (fatty – mixed – calcified) and it is potentially able to detect IPH.13,18-20 In particular, the introduction of multi-energy21 technology further increases the capabilities of CT in the detection and characterization of carotid atherosclerosis. Advantages of multi-energy CT compared with conventional CT include the ability to differentiate calcified plaque from iodinated contrast, while also facilitating bone subtraction. Limitations of CT are mainly related to the radiation dose delivered to the patients and to the potential side effects of contrast materials.13,22,23 In the last years, several papers have been published using positron emission tomography (PET)-CT which can identify various functional images.24 For PET, the most commonly used tracer is 18F-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose (18F-FDG). PET-18F-FDG allows the measurement of metabolic activity in atherosclerotic plaques, which correlates with plaque macrophage infiltration and vascular endothelial growth factor. Another tracer introduced is 18F-fluorocholine (18F-FCH). Choline is a precursor of phosphatidylcholine, a key component of all cellular membranes and correlates strongly with degree of macrophage infiltration and recent symptoms.25 Also nanoparticles are being used for molecular imaging of atherosclerosis and in particular iron oxide MRI contrast agents provide highly efficient iron-labeling in macrophages for magnetic resonance-based detection in vivo24 and were reported as very promising in the detection of plaque inflammation.25
MRI is currently considered the most favorable non-invasive imaging technique (Fig. 3) to characterize features of plaque vulnerability such as intra-plaque hemorrhage IPH, LRNC, and the status of the FC.26
MR allows for the accurate distinction of plaque components27 such as the LRNC, fibrous tissue, and IPH exploiting their different signal properties. While the identification of calcified components can be more challenging compared to CT, MR still offers usually good results. MR plaque imaging is usually combined with an MR angiography which provides information about the luminal morphology, including plaque ulceration. This can be either a time-of-flight MRA, which does not require the injection of a contrast medium, or a contrast-enhanced MRA, which is acquired during the first pass of an i.v. gadolinium bolus.
It is noteworthy that initial research in carotid plaque MR imaging relied on carotid surface coils to provide high-resolution images of the plaque and vessel wall. This was initially considered a limitation because of the lack of availability of such coils in routine clinical practice and the challenges related to adequate positioning of carotid surface coils due to their small coverage.28 However, recently published studies using 3T MRI scanners with conventional neurovascular coils showed promising results in terms of identifying LRNC and IPH,28 even though further data with bigger populations are necessary to corroborate these findings. Drawbacks of MR are the relatively long study times and the sensitivity of image quality to motion effects.
Advanced MR protocols including dynamic contrast enhancement (DCE) allow quantification of plaque vascularity by using gadolinium contrast agents together with pharmacokinetic modeling.29 Moreover, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms is allowing to improve the general performances.30,31
Maximum wall thickness (MWT) represents the maximum thickness of the plaque. This feature can be quantified by US, CT and MRI and is associated with features of plaque vulnerability, such as IPH and status of the FC.32 In a study published in 2017, based on 1,072 symptomatic subjects that underwent MRI of carotid arteries, the MWT was more strongly associated with cerebral ischemic symptoms (AUC=0.93; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.91–0.95) than was the degree of stenosis (AUC=0.81; 95% CI: 0.76–0.84).33 The use of advanced techniques34,35 in MR imaging allow to better define the carotid plaque with subsequent plaque thickness quantification.
Another parameter that is simple to characterize on CT and MRI is plaque length. Plaque length does not appear to relate directly to the occurrence of cerebrovascular events, but it is an independent risk factor for peri-procedural complications and excessive re-stenosis rate in carotid interventions.36
The morphology of the luminal surface of carotid plaques is considered a risk feature of cerebrovascular events.3 In particular, the presence of ulceration (Fig. 4) significantly increases the risk of cerebrovascular events. Conventional US is generally not considered an optimal technique for the detection of irregular plaque surface and ulcerations, but 3D US and CEUS have recently proved effective for this purpose.37 CT and MR offer very good results in detecting ulcerations when compared to histopathology, with performance significantly superior to that of US.38
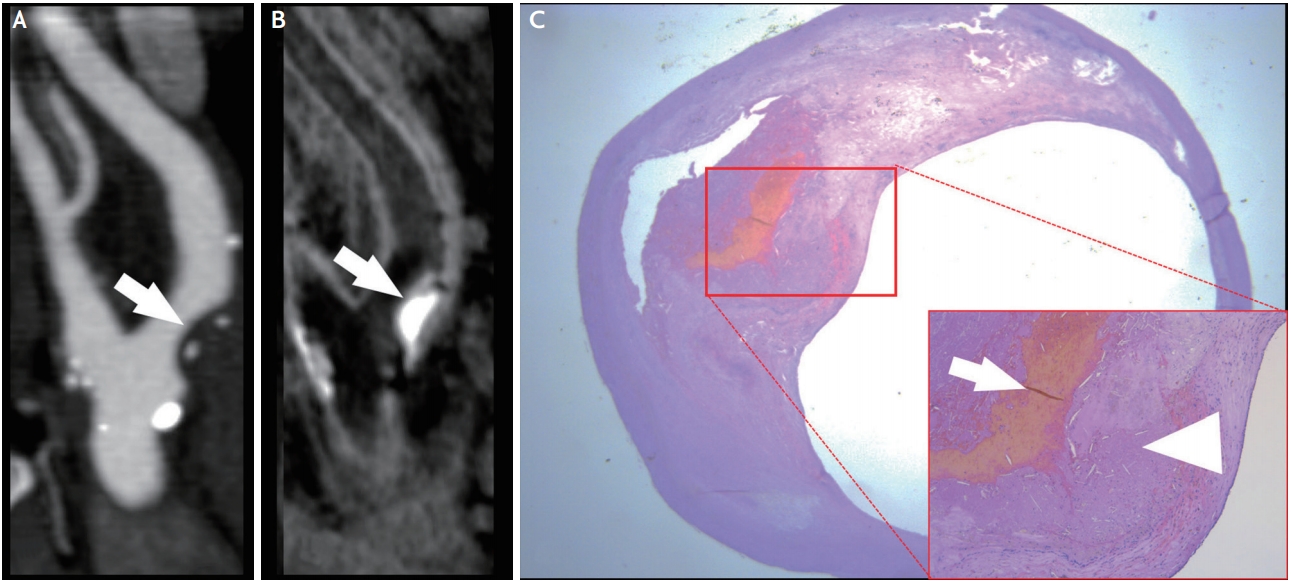
Nowadays IPH is considered one of the identifying features of vulnerable plaque39,40 and several meta-analyses indicate that MRI detection of carotid IPH is associated with increased risk for future ischemic cerebrovascular events in patients with carotid stenosis.41 Among all available imaging techniques, MRI is preferred (Fig. 5) for the detection of IPH because its imaging depends on the oxidative state of hemoglobin,30 which is easily detected on MR via common imaging protocols (e.g T1-MPRAGE or T1-turbo spin echo with fat saturation).18 It is worth noting that dedicated carotid wall imaging with small field-of-view (FOV) surface coils are not needed for the detection of IPH, since this can be achieved at lower spatial resolution using large FOV neck coils.28 CT shows conflicting results in the literature, with some authors going as far to suggest that even low Hounsfield unit (HU) values (<25 HU)42 may associate with the presence of IPH.
Lipids are one of the key components of atherosclerotic plaques and the size of the LRNC in carotid plaques is believed to be predictive of increased risk of a cerebrovascular event.41 A recent study identified a threshold of 40% LRNC as being associated with an increased risk for occurrence of cerebrovascular events.42 A CT versus MRI comparison (Fig. 5) study reported that the best imaging feature for detection of a complicated AHA type VI plaque by MRI was the thickness of the soft plaque component by CT (receiver operator characteristic area under the curve=0.89).43 Both CT and MR can identify the presence of lipid components thanks to lipid-tissue attenuation properties and signal characteristics.
The FC is a layer of fibrous connective tissue which separates the core of the plaque from the arterial lumen. FC alterations (thin or ruptured cap) are considered an important feature of plaque vulnerability.44 An intact FC is associated with a low risk of occurrence of cerebrovascular events whereas a ruptured FC is associated with a high risk of events.44 By considering non-invasive imaging (therefore excluding intravascular ultrasound), MRI is considered the preferred technique to image this feature for the carotid artery, especially with the use of gadolinium.45
Inflammation is a key factor in the pathophysiology of atherosclerosis with regard to progression and destabilization of plaques. Compared to stable lesions, rupture-prone or vulnerable plaques typically exhibit inflammation and intra-plaque neovascularization.5 The pro-inflammatory state caused by endothelial cell dysfunction promotes the expression of cellular adhesion molecules and consequently the recruitment of inflammatory cells (mainly macrophages).5 A significant correlation between macrophage plaque infiltration, plaque rupture and ischemic symptoms exists.5,25 Inflammatory cells accumulate in specific areas of the plaque, typically the shoulder or in the FC.
Another important feature is intra-plaque neovascularization. As the plaque size increases, oxygen levels deep within the plaque diminish, and local hypoxia triggers microvessel formation into the intima through breaks in the media. These neovessels are characterized by an immature endothelial lining and may lead to bleeding in the plaque (IPH). Therefore, the degree of intra-plaque neovascularization is linked to the “activity” of the plaque in terms of inflammation and increased risk of neovessel rupture and hemorrhage (IPH).46,47
CEUS and MR are highly correlated in terms of detecting intra-plaque neovascularization. CT can also help with the detection of intra-plaque neovascularization and in its quantification as the amount of contrast enhancement on CT is associated with the extent of neovascularization.48-50
On MRI, enhancement of the carotid plaque after the administration of gadolinium is associated with neovascularization (p<0.001). There is a correlation between the degree of plaque enhancement and the degree of neovascularization.51 DCE-MR permits quantification of plaque vascularity29 and plaque perfusion and it has been shown to give reproducible physiological measurements of the vasa vasorum. However, as mentioned above, one of the main limitations of DCE-MR is that the vessel wall is difficult to image dynamically because of its small size and motion artifacts.
The volume of the carotid artery plaque may be associated with vulnerability of the plaque.52 Measurement of this feature is facilitated by recent software packages for volumetric analysis. Recent papers showed that the volume of the carotid artery plaque is associated with the occurrence of cardiovascular events.53 Evidence indicates that increasing plaque volume is associated with an increase in lipid and calcium components.53 Because of the excellent spatial resolution of CT, it is possible to calculate accurately the total plaque volume and also the volume of the sub-components of the plaque according to the attenuation values of the voxels.54 Similarly, MRI proved useful for plaque component volume quantification55 even though the spatial resolution of MRI is lower than that of CT.
On the one hand, the efficacy of carotid revascularization in stroke prevention in symptomatic individuals with 50 to 99% carotid stenosis is documented but, on the other hand, 70 to 80% of symptomatic patients with >50% stenosis will not experience a recurrent stroke at 5 years.56 This group of patients at relatively low risk of recurrent cerebral ischemic events routinely undergo surgical intervention which will often be unnecessary, demonstrating the limitation of the current risk stratification model, based on degree of stenosis alone.57 It has been demonstrated that early initiation of medical therapy after transient ischemic attack (TIA) or minor stroke significantly lowers the risk of stroke recurrence.58 Therefore, identifying patients at risk of stroke despite modern medical therapy has become increasingly important. Nonetheless, the choice of the correct therapy is debated and some guidelines recommend expanding the indications for carotid revascularization in carotid disease. A risk model which takes into account multiple clinical and demographic patient characteristics in addition to the degree of stenosis represents a step forward in identifying patients at risk of stroke. Inclusion of carotid imaging features into such risk models has the potential to further improve the selection of individual patients for treatment.
The impact of plaque imaging is considered in the recently published guidelines and perspectives. In particular, the perspective and guidelines from the American Society of Neuroradiology vessel wall imaging study group and expert consensus recommendations of the American Society of Neuroradiology, released in February 2018,13 focused on the technological implications and impact of the imaging technologies for the carotid plaque imaging. In this document it is suggested that for carotid artery imaging some technological thresholds are necessary, and in particular for the CT at least a 32-detector-row CT scanner whereas for the MR at least a 1.5T with carotid coil or a 3T system (with or without dedicated carotid coil); moreover in order to obtain the necessary level of information by using the MR a minimum set of sequences are needed and are described in the document. In the “guidelines on diagnosis and treatment of peripheral artery disease”, released by the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)58 in March 2018, it is recommended that for asymptomatic patients with a life expectancy >5 years and 60-99% carotid artery stenosis and imaging features associated with increased risk of ipsilateral stroke (IPH or LRNC), carotid artery revascularization should be considered: carotid endarterectomy (CEA) if they are considered “average surgical risk” (class of recommendation: IIa; level of recommendation: B) and carotid artery stenting if they are considered “high risk for CEA” (class of recommendation: IIa; level of recommendation: B). Ongoing trials will provide further evidence on whether carotid plaque imaging identifies patients who benefit from revascularization. The AHA produced a guideline completely dedicated to the management of patients with extracranial carotid and vertebral artery disease in 2011,59 where the key parameters for the choice of the treatment were the stenosis and the presence of absence of cerebrovascular symptoms. However, new updated version is currently ongoing because of the time occurred from the previous one.
The identification of protective imaging features in carotid artery plaques represents a future goal for carotid plaque imaging. In the literature, the protective effect of heavily calcified plaque is described; however, a recent study using energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis identified two types of calcium salts in atheromatous plaques, hydroxyapatite and calcium oxalate. The authors showed an association between hydroxyapatite calcification and unstable plaques whereas calcium oxalate calcifications were mainly detected in stable plaques.60 This finding could widen the utilization of multi-energy CT scanners because of their potential to perform spectral analysis and distinguish between the different subtypes of calcifications61 with the potential for further risk stratification.
Plaque volume seems to be a promising parameter related to the risk of recurrent TIA or stroke. In 2018 Lu et al.62 demonstrated that the annual progression of carotid plaque volume is independently associated with recurrent ischemic cerebrovascular events, and this measurement added value to the presence of IPH and FC rupture in terms of predicting future events. Atherosclerotic plaque volume progression and composition can facilitate the rupture of the plaques.52 Therefore, monitoring plaque volume changes may improve our ability to estimate risk and monitor the effect of medical therapy.
Medical therapy with anti-inflammatory drugs and high-dose statin showed very good results in reducing the occurrence of cardio- and cerebro-vascular events. Monitoring the effect of such medical therapy on the plaque, by checking on the progression and regression patterns, could represent a key element in the selection of the optimal therapy, especially in the light of the different plaque risk profiles independent of the degree of stenosis.
It is likely that a strategy combining more than one approach will prove most valuable, as the different approaches are complementary to each other. Future studies comparing different modalities of plaque imaging will be helpful from this perspective.
AI is booming in all areas of business and medicine.63 Recent advances in the field of AI have opened up new avenues for creating novel modeling and predictive methods for clinical use. The recent explosion of imaging data is creating a path for such approaches because of the huge amount of information included in CT and MR imaging datasets. Deep learning may provide the ability to identify patterns of imaging information and improve risk stratification.64
Several prospective studies (ARIC, MESA, PARISK, CAPIAS, CARE-II, CAIN)9,43,57,65-70 are currently ongoing to assess the value of plaque imaging in stroke risk stratification. Ongoing randomized trials comparing best medical therapy alone versus carotid revascularization either select patients (such as ACTRIS) or allow to measure the benefit of revascularization (such as ECST-2) based on carotid plaque MRI or other extended imaging.
Carotid artery plaques are heterogeneous in terms of biology, pathology and vulnerability with different therapeutic implications based on their features. Imaging plays a key role in the evaluation of patients with atherosclerotic carotid disease because it allows for characterization of the plaque structure and composition. Advanced imaging for the characterization of carotid plaque vulnerability can help refine risk stratification and allow for individualization of care. Further evaluation in randomized clinical trials is needed to establish the exact role of plaque imaging in clinical decision-making.
Fig. 1.
Male patient with <50% right internal carotid artery stenosis due to a fatty plaque. The magnetic resonance images in (A) T1W, (B) STIR and (C) T2W shows the presence of a carotid artery plaque (white arrow).

Fig. 2.
Male patient with hand weakness with <50% stenosis in the internal carotid artery. (A, B) The computed tomography axial images in different planes shows the presence of a carotid plaque with automated volumes segmentation (white arrow).
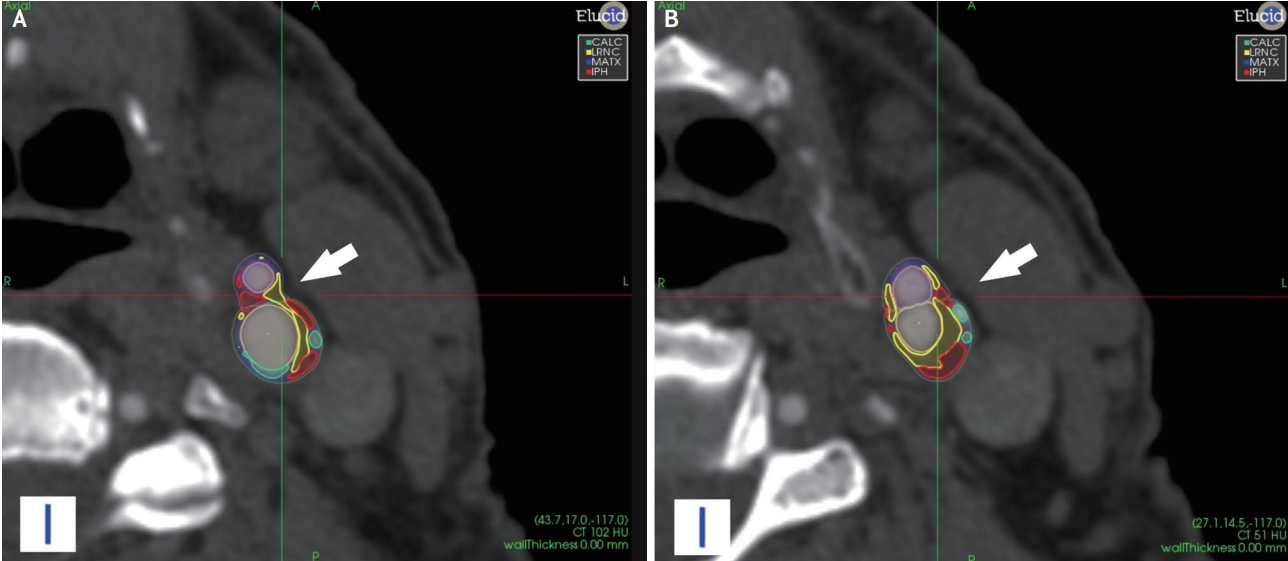
Fig. 3.
Female patient. The magnetic resonance time-of-flight shows the (A) common carotid artery (white arrow) and (B) the internal (white arrow) and (C) external (white open arrowhead) and internal (white arrowhead) carotid artery.
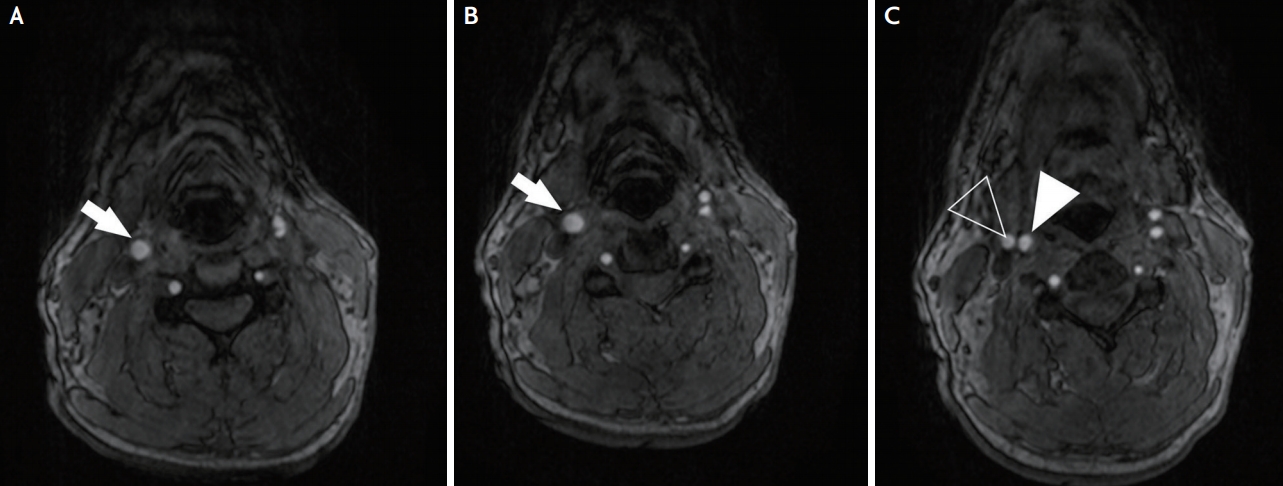
Fig. 4.
Male patient with right hand weakness with ulceration in the (A) left internal carotid artery internal carotid artery visibile in the sagittal, (B) axial and (C) Coronal planes (white arrows).

Fig. 5.
Male patient with left hand weakness with intra-plaque hemorrhage and lipid-rich-necrotic-core in the right internal carotid artery. In the (A) CTA and (B) magnetic resonance, it is visible the presence of IPH (white arrows). The patient underwent carotid endarterectomy and the ntraplaque hemorrhage is visible in the (C) histopathology section (white arrow). The arrowhead shows the fibrous cap.
REFERENCES
1. Ooi YC, Gonzalez NR. Management of extracranial carotid artery disease. Cardiol Clin. 2015;33:1-35.



2. Yanez ND, Burke GL, Manolio T, Gardin JM, Polak J; CHS Collaborative Research Group. Sibling history of myocardial infarction or stroke and risk of cardiovascular disease in the elderly: the cardiovascular health study. Ann Epidemiol. 2009;19:858-866.



3. Barnett HJ, Taylor DW, Eliasziw M, Fox AJ, Ferguson GG, Haynes RB, et al. Benefit of carotid endarterectomy in patients with symptomatic moderate or severe stenosis. North American symptomatic carotid endarterectomy trial collaborators. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1415-1425.


4. Rothwell PM, Eliasziw M, Gutnikov SA, Fox AJ, Taylor DW, Mayberg MR, et al. Analysis of pooled data from the randomised controlled trials of endarterectomy for symptomatic carotid stenosis. Lancet. 2003;361:107-116.


5. Redgrave JN, Lovett JK, Gallagher PJ, Rothwell PM. Histological assessment of 526 symptomatic carotid plaques in relation to the nature and timing of ischemic symptoms: the Oxford plaque study. Circulation. 2006;113:2320-2328.


6. Saba L, Saam T, Jäger HR, Yuan C, Hatsukami TS, Saloner D, et al. Imaging biomarkers of vulnerable carotid plaques for stroke risk prediction and their potential clinical implications. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18:559-572.


7. Wasserman BA, Wityk RJ, Trout HH 3rd, Virmani R. Lowgrade carotid stenosis: looking beyond the lumen with MRI. Stroke. 2005;36:2504-2513.


8. Pletsch-Borba L, Selwaness M, van der Lugt A, Hofman A, Franco OH, Vernooij MW. Change in carotid plaque components: a 4-year follow-up study with serial MR imaging. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018;11:184-192.


9. Zavodni AE, Wasserman BA, McClelland RL, Gomes AS, Folsom AR, Polak JF, et al. Carotid artery plaque morphology and composition in relation to incident cardiovascular events: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis (MESA). Radiology. 2014;271:381-389.



10. Zhao XQ, Hatsukami TS, Hippe DS, Sun J, Balu N, Isquith DA, et al. Clinical factors associated with high-risk carotid plaque features as assessed by magnetic resonance imaging in patients with established vascular disease (from the AIM-HIGH study). Am J Cardiol. 2014;114:1412-1419.



11. Naghavi M, Libby P, Falk E, Casscells SW, Litovsky S, Rumberger J, et al. From vulnerable plaque to vulnerable patient: a call for new definitions and risk assessment strategies: part II. Circulation. 2003;108:1772-1778.


12. Saba L, Anzidei M, Marincola BC, Piga M, Raz E, Bassareo PP, et al. Imaging of the carotid artery vulnerable plaque. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2014;37:572-585.



13. Saba L, Yuan C, Hatsukami TS, Balu N, Qiao Y, DeMarco JK, et al. Carotid artery wall imaging: perspective and guidelines from the ASNR vessel wall imaging study group and expert consensus recommendations of the American Society of Neuroradiology. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2018;39:E9-E31.



14. Saba L, Argioas GM, Lucatelli P, Lavra F, Suri JS, Wintermark M. Variation of degree of stenosis quantification using different energy level with dual energy CT scanner. Neuroradiology. 2019;61:285-291.



15. Baradaran H, Ng CR, Gupta A, Noor NM, Al-Dasuqi KW, Mtui EE, et al. Extracranial internal carotid artery calcium volume measurement using computer tomography. Int Angiol. 2017;36:445-461.


16. Saba L, Sanfilippo R, Balestrieri A, Zaccagna F, Argiolas GM, Suri JS, et al. Relationship between carotid computed tomography dual-energy and brain leukoaraiosis. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017;26:1824-1830.


17. Saba L, Bhavsar AV, Gupta A, Mtui EE, Giambrone AE, Baradaran H, et al. Automated calcium burden measurement in internal carotid artery plaque with CT: a hierarchical adaptive approach. Int Angiol. 2015;34:290-305.

18. Porcu M, Anzidei M, Suri JS, A Wasserman B, Anzalone N, Lucatelli P, et al. Carotid artery imaging: the study of intra-plaque vascularization and hemorrhage in the era of the “vulnerable” plaque. J Neuroradiol. 2019 Apr 4;[Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurad.


19. Saba L, Lanzino G, Lucatelli P, Lavra F, Sanfilippo R, Montisci R, et al. Carotid plaque CTA analysis in symptomatic subjects with bilateral intraparenchymal hemorrhage: a preliminary analysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019;40:1538-1545.



20. Saba L, Micheletti G, Brinjikji W, Garofalo P, Montisci R, Balestrieri A, et al. Carotid intraplaque-hemorrhage volume and its association with cerebrovascular events. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019 Sep 26;[Epub]. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A6189.

21. Saba L, Argiolas GM, Siotto P, Piga M. Carotid artery plaque characterization using CT multienergy imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013;34:855-859.



22. Sahbaee P, Segars WP, Marin D, Nelson RC, Samei E. The effect of contrast material on radiation dose at CT: part I. incorporation of contrast material dynamics in anthropomorphic phantoms. Radiology. 2017;283:739-748.


23. Sahbaee P, Abadi E, Segars WP, Marin D, Nelson RC, Samei E. The effect of contrast material on radiation dose at CT: part II. A systematic evaluation across 58 patient models. Radiology. 2017;283:749-757.


24. Hyafil F, Schindler A, Sepp D, Obenhuber T, Bayer-Karpinska A, Boeckh-Behrens T, et al. High-risk plaque features can be detected in non-stenotic carotid plaques of patients with ischaemic stroke classified as cryptogenic using combined (18)F-FDG PET/MR imaging. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016;43:270-279.



25. Vöö S, Kwee RM, Sluimer JC, Schreuder FH, Wierts R, Bauwens M, et al. Imaging intraplaque inflammation in carotid atherosclerosis with 18F-fluorocholine positron emission tomography-computed tomography: prospective study on vulnerable atheroma with immunohistochemical validation. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016;9(5.

26. Chen S, Zhao H, Li J, Zhou Z, Li R, Balu N, et al. Evaluation of carotid atherosclerotic plaque surface characteristics utilizing simultaneous noncontrast angiography and intraplaque hemorrhage (SNAP) technique. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018;47:634-639.


27. Cai J, Hatsukami TS, Ferguson MS, Kerwin WS, Saam T, Chu B, et al. In vivo quantitative measurement of intact fibrous cap and lipid-rich necrotic core size in atherosclerotic carotid plaque: comparison of high-resolution, contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and histology. Circulation. 2005;112:3437-3444.


28. Brinjikji W, DeMarco JK, Shih R, Lanzino G, Rabinstein AA, Hilditch CA, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of a clinical carotid plaque MR protocol using a neurovascular coil compared to a surface coil protocol. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018;48:1264-1272.


29. Yuan J, Makris G, Patterson A, Usman A, Das T, Priest A, et al. Relationship between carotid plaque surface morphology and perfusion: a 3D DCE-MRI study. MAGMA. 2018;31:191-199.



30. Saba L, Gao H, Raz E, Sree SV, Mannelli L, Tallapally N, et al. Semiautomated analysis of carotid artery wall thickness in MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2014;39:1457-1467.


31. van ‘t Klooster R, de Koning PJ, Dehnavi RA, Tamsma JT, de Roos A, Reiber JH, et al. Automatic lumen and outer wall segmentation of the carotid artery using deformable three-dimensional models in MR angiography and vessel wall images. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;35:156-165.


32. Underhill HR, Hatsukami TS, Cai J, Yu W, DeMarco JK, Polissar NL, et al. A noninvasive imaging approach to assess plaque severity: the carotid atherosclerosis score. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;3:1068-1075.

33. Zhao X, Hippe DS, Li R, Canton GM, Sui B, Song Y, et al. Prevalence and characteristics of carotid artery high-risk atherosclerotic plaques in Chinese patients with cerebrovascular symptoms: a Chinese atherosclerosis risk evaluation II study. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017;6(8.

34. Liu H, Sun J, Hippe DS, Wu W, Chu B, Balu N, et al. Improved carotid lumen delineation on non-contrast MR angiography using SNAP (simultaneous non-contrast angiography and intraplaque hemorrhage) imaging. Magn Reson Imaging. 2019;62:87-93.



35. Moerman AM, Dilba K, Korteland S, Poot DHJ, Klein S, van der Lugt A, et al. An MRI-based method to register patient-specific wall shear stress data to histology. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0217271.



36. Bonati LH, Ederle J, Dobson J, Engelter S, Featherstone RL, Gaines PA, et al. Length of carotid stenosis predicts peri-procedural stroke or death and restenosis in patients randomized to endovascular treatment or endarterectomy. Int J Stroke. 2014;9:297-305.


37. Saha SA, Gourineni V, Feinstein SB. The use of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for imaging of carotid atherosclerotic plaques: current evidence, future directions. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2016;26:81-96.


38. Saba L, Caddeo G, Sanfilippo R, Montisci R, Mallarini G. Efficacy and sensitivity of axial scans and different reconstruction methods in the study of the ulcerated carotid plaque using multidetector-row CT angiography: comparison with surgical results. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28:716-723.


39. Altaf N, Daniels L, Morgan PS, Auer D, MacSweeney ST, Moody AR, et al. Detection of intraplaque hemorrhage by magnetic resonance imaging in symptomatic patients with mild to moderate carotid stenosis predicts recurrent neurological events. J Vasc Surg. 2008;47:337-342.


40. Hatsukami TS, Yuan C. MRI in the early identification and classification of high-risk atherosclerotic carotid plaques. Imaging Med. 2010;2:63-75.



41. Gupta A, Baradaran H, Schweitzer AD, Kamel H, Pandya A, Delgado D, et al. Carotid plaque MRI and stroke risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2013;44:3071-3077.


42. Saba L, Francone M, Bassareo PP, Lai L, Sanfilippo R, Montisci R, et al. CT attenuation analysis of carotid intraplaque hemorrhage. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2018;39:131-137.



43. Trelles M, Eberhardt KM, Buchholz M, Schindler A, Bayer-Karpinska A, Dichgans M, et al. CTA for screening of complicated atherosclerotic carotid plaque--American Heart Association type VI lesions as defined by MRI. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013;34:2331-2337.



44. Demarco JK, Ota H, Underhill HR, Zhu DC, Reeves MJ, Potchen MJ, et al. MR carotid plaque imaging and contrast-enhanced MR angiography identifies lesions associated with recent ipsilateral thromboembolic symptoms: an in vivo study at 3T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31:1395-1402.



45. Yuan C, Kerwin WS, Ferguson MS, Polissar N, Zhang S, Cai J, et al. Contrast-enhanced high resolution MRI for atherosclerotic carotid artery tissue characterization. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2002;15:62-67.


46. Truijman MT, Kwee RM, van Hoof RH, Hermeling E, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Mess WH, et al. Combined 18F-FDG PET-CT and DCE-MRI to assess inflammation and microvascularization in atherosclerotic plaques. Stroke. 2013;44:3568-3570.


47. Virmani R, Kolodgie FD, Burke AP, Finn AV, Gold HK, Tulenko TN, et al. Atherosclerotic plaque progression and vulnerability to rupture: angiogenesis as a source of intraplaque hemorrhage. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25:2054-2061.


48. Shah BN, Chahal NS, Kooner JS, Senior R. Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography vs B-mode ultrasound for visualization of intima-media thickness and detection of plaques in human carotid arteries. Echocardiography. 2017;34:723-730.


49. Huang R, Abdelmoneim SS, Ball CA, Nhola LF, Farrell AM, Feinstein S, et al. Detection of carotid atherosclerotic plaque neovascularization using contrast enhanced ultrasound: a systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy studies. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2016;29:491-502.


50. Saba L, Lai ML, Montisci R, Tamponi E, Sanfilippo R, Faa G, et al. Association between carotid plaque enhancement shown by multidetector CT angiography and histologically validated microvessel density. Eur Radiol. 2012;22:2237-2245.



51. Qiao Y, Etesami M, Astor BC, Zeiler SR, Trout HH 3rd, Wasserman BA. Carotid plaque neovascularization and hemorrhage detected by MR imaging are associated with recent cerebrovascular ischemic events. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012;33:755-760.



52. Anzidei M, Suri JS, Saba L, Sanfilippo R, Laddeo G, Montisci R, et al. Longitudinal assessment of carotid atherosclerosis after radiation therapy using computed tomography: a case control study. Eur Radiol. 2016;26:72-78.



53. Saba L, Sanfilippo R, Sannia S, Anzidei M, Montisci R, Mallarini G, et al. Association between carotid artery plaque volume, composition, and ulceration: a retrospective assessment with MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012;199:151-156.


54. Adraktas DD, Tong E, Furtado AD, Cheng SC, Wintermark M. Evolution of CT imaging features of carotid atherosclerotic plaques in a 1-year prospective cohort study. J Neuroimaging. 2014;24:1-6.


55. Wasserman BA, Astor BC, Sharrett AR, Swingen C, Catellier D. MRI measurements of carotid plaque in the atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study: methods, reliability and descriptive statistics. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010;31:406-415.



56. Fairhead JF, Mehta Z, Rothwell PM. Population-based study of delays in carotid imaging and surgery and the risk of recurrent stroke. Neurology. 2005;65:371-375.


57. Naylor AR. What is the current status of invasive treatment of extracranial carotid artery disease? Stroke. 2011;42:2080-2085.


58. Aboyans V, Ricco JB, Bartelink MEL, Björck M, Brodmann M, Cohnert T, et al. ESC scientific document group. 2017 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of peripheral arterial diseases, in collaboration with the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS): document covering atherosclerotic disease of extracranial carotid and vertebral, mesenteric, renal, upper and lower extremity arteries endorsed by: the European Stroke Organization (ESO) the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of peripheral arterial diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and of the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS). Eur Heart J. 2018;39:763-816.



59. Brott TG, Halperin JL, Abbara S, Bacharach JM, Barr JD, Bush RL, et al. 2011 ASA/ACCF/AHA/AANN/AANS/ACR/ASNR/CNS/SAIP/SCAI/SIR/SNIS/SVM/SVS guideline on the management of patients with extracranial carotid and vertebral artery disease: executive summary. A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association task force on practice guidelines, and the American Stroke Association, American Association of Neuroscience Nurses, American Association of Neurological Surgeons, American College of Radiology, American Society of Neuroradiology, Congress of Neurological Surgeons, Society of Atherosclerosis Imaging and Prevention, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Society of Interventional Radiology, Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery, Society for Vascular Medicine, and Society for Vascular Surgery. Stroke. 2011;124:489-532.
60. Bischetti S, Scimeca M, Bonanno E, Federici M, Anemona L, Menghini R, et al. Carotid plaque instability is not related to quantity but to elemental composition of calcification. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2017;27:768-774.


61. Kirkbride TE, Raja AY, Müller K, Bateman CJ, Becce F, Anderson NG. Discrimination between calcium hydroxyapatite and calcium oxalate using multienergy spectral photon-counting CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017;209:1088-1092.


62. Lu M, Peng P, Cui Y, Qiao H, Li D, Cai J, et al. Association of progression of carotid artery wall volume and recurrent transient ischemic attack or stroke: a magnetic resonance imaging study. Stroke. 2018;49:614-620.


63. Saba L, Biswas M, Kuppili V, Cuadrado Godia E, Suri HS, Edla DR, et al. The present and future of deep learning in radiology. Eur J Radiol. 2019;114:14-24.


64. Araki T, Ikeda N, Shukla D, Londhe ND, Shrivastava VK, Banchhor SK, et al. A new method for IVUS-based coronary artery disease risk stratification: a link between coronary & carotid ultrasound plaque burdens. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2016;124:161-179.


65. Bayer-Karpinska A, Schwarz F, Wollenweber FA, Poppert H, Boeckh-Behrens T, Becker A, et al. The carotid plaque imaging in acute stroke (CAPIAS) study: protocol and initial baseline data. BMC Neurol. 2013;13:201.




66. Truijman MT, Kooi ME, van Dijk AC, de Rotte AA, van der Kolk AG, Liem MI, et al. Plaque at RISK (PARISK): prospective multicenter study to improve diagnosis of high-risk carotid plaques. Int J Stroke. 2014;9:747-754.


67. Tardif JC, Spence JD, Heinonen TM, Moody A, Pressacco J, Frayne R, et al. Atherosclerosis imaging and the Canadian atherosclerosis imaging network. Can J Cardiol. 2013;29:297-303.


68. Ikram MA, van der Lugt A, Niessen WJ, Koudstaal PJ, Krestin GP, Hofman A, et al. The rotterdam scan study: design update 2016 and main findings. Eur J Epidemiol. 2015;30:1299-1315.




-
METRICS

-
- 2 Crossref
- Scopus
- 7,710 View
- 275 Download
- Related articles in AC






