 |
 |
- Search
| J Neurosonol Neuroimag > Volume 10(2); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background
In patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD), one of the common non-motor symptoms is depression. Recent studies demonstrate that the rate of decreased echogenicity in the brainstem raphe (BR) is significantly higher in patients with PD with depression. The objective of this study was to investigate the feasibility of transcranial sonographic measurements of mesencephalic midline change in Korean patients with PD. We also questioned that there may be any differences regarding to the rate of poor temporal window (TW) between transcranial sonography and transcranial Doppler (TCD) examination.
Methods
Patients were eligible for the study if they had de novo PD and were 40 years of age or older. High-resolution B-mode ultrasound measurements of the BR were performed using a Siemens Acuson S1000 scanner (Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany) with a 2.0-3.5 MHz transducer. Reliability was estimated by Cohen’s kappa coefficient, in order to measure the degree of intra- and interobserver agreement.
Results
A total of 200 patients with PD were recruited for the study. Of these 200 patients, BR echogenicity could not be measured in 49 patients (24.5%), due to a bilateral poor TW. Compared to other TCD studies, the poor TW rate in our patient sample is lower than that found in previous studies conducted in Asian populations, including a Korean study showing a poor TW rate of 34%. A poor TW was significantly more frequent in women than men (37.6% vs. 6%, p<0.0001). The overall kappa value was excellent (к>0.8). Intra- and interobserver reliability was 0.842 and 0.821, respectively.
In patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD), one of the common non-motor symptoms is depression. Significant depressive events are known to occur in 40-50% of patients with PD throughout their clinical course [1]. The onset of depression is not concurrent with the recognition of motor symptoms, and may show as an early manifestation of PD. Also, premorbid depression is known to be more frequent in patients with PD than in the general population [2]. The raphe nucleus (RN) is a structure of the serotonergic system, in the midline of the brainstem, which is involved in depression. Thus, as depression is a predictor for the development of PD, finding abnormalities in the mesencephalic midline may be a useful diagnostic approach [3].
Transcranial sonography (TCS) is a non-invasive neuroimaging procedure that can be applied in the bedside environment. Becker et al. [4] were the first to report hypoechogenicity of brainstem raphe (BR) as a characteristic TCS finding in depressed PD patients. Since then, several studies confirm that the rate of decreased echogenicity in the BR is significantly higher in patients with PD with depression [3,5,6]. A standardized protocol, based on accepted TCS practice, is essential for the clinical study using TCS. Standardized scanning procedure can achieve comparability of TCS findings between different study groups. However, an exact methodology of measuring echogenicity in the BR in Korean patients with PD has not been appropriately described. The objective of this study was to investigate the feasibility of transcranial sonographic measurements of mesencephalic midline change in Korean patients with PD. We also questioned that there may be any differences regarding to the rate of poor temporal window (TW) between TCS and transcranial Doppler (TCD) examination.
Between January 2015 and January 2018, patients presenting to the PD clinic of the Sanggye Paik Hospital were enrolled in this study. Patients were eligible for the study if they had de novo PD and were 40 years of age or older. The criteria of the UK Parkinson’s Disease Society Brain Bank were strictly used for the diagnosis of PD [7]. The patients’ demographics, the progression of their symptoms, and their motor disabilities were documented at baseline.
As a result of a first consensus meeting of the European Society of Neurosonology and Cerebral Hemodynamics 2004, a state-of-the-art examination protocol was established. Subsequently, updates on methodological standards including definitions of clear quality criteria of adequate TCS imaging were provided [5]. For the study, high-resolution B-mode ultrasound measurements of the BR were performed using a Siemens Acuson S1000 scanner (Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany) with a 2.0-3.5 MHz transducer. TCS modes were set at an image depth of 14-16 cm and a dynamic range of 45-60 dB. Low echo signal suppression, time gain compensation, and brightness were adjusted as needed. With the patient in a supine position, BR echogenicity is observable by scanning through the preauricular transtemporal bone window. At the axial scanning plane, the image can be set at the midbrain level. After finding a butterfly-shaped mesencephalic midline and freezing the image, BR echogenicity was evaluated semiquantitatively (Fig. 1). The reference point for rating BR echogenicity was the adjacent highly echogenic red nucleus. A three-point scale was used for this study. A rating of grade I was given when the BR was not visible. Grade II indicated slightly echogenic or interrupted BR, and grade III was applied for normal or higher BR echogenicity. Subjects were examined on both sides, since transtemporal windows are not always symmetric. The higher score of two bilateral measurements was chosen as the BR echogenicity grade.
An experienced physician conducted all measurements according to a standardized manual of operations. The BR was measured consecutively at different days to assess intraobserver variability (H.W.K.), and then graded by three different observers (H.W.K., H.R.Y., and S.W.H.) to estimate interobserver variability. All subjects provided signed informed consent, and the study was approved by the local institutional review board.
Data are expressed as mean±standard deviation or as numbers (%) unless otherwise indicated. The Student’s t-test was used to compare normally distributed data and the Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare non-normally distributed data. Categorical data were examined using chi square analysis. Reliability was estimated by Cohen’s kappa coefficient, in order to measure the degree of intra- and interobserver agreement. Two-sided null hypotheses of no difference were rejected if p-values were lower than 0.05. SPSS version 20.0 for Windows (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA) was used for statistical analysis.
A total of 200 patients with PD were recruited for the study. Their mean age was 68.2 years (range, 41-92) and 117 patients were women (58.5%). Table 1 shows the baseline characteristics of the enrolled patients grouped by visibility of the TW. Of all 200 patients, BR echogenicity could not be measured in 49 patients (24.5%), due to a bilateral poor TW. A poor TW was significantly more frequent in woman than men (37.6% vs. 6%, p<0.0001). Table 2 demonstrates the baseline characteristics of the patients grouped by TW and sex. No significant differences were observed in these characteristics between groups.
Intra- and interobserver reliability was analyzed using kappa statistic. The overall kappa value was excellent (k>0.8). Intra- and interobserver reliability was 0.842 and 0.821, respectively. Intraobserver differences were observed in seven patients; all cases were between grade II and III. Interobserver disagreement was observed in 14 patients. Two were between grade I and II, and all other cases were between grade II and III. There were no cases where all three physicians disagreed with each other.
In this study, we investigated the feasibility of transcranial sonographic measurements of BR echogenicity in Korean patients with PD. We tested its ease of use and the inter-rater reliability in this study. The first measurement and discovery of decreased BR echogenicity in depressed patients using TCS was reported in 1994 [8]. Since then, several studies based on the same concept were conducted; one study has confirmed the interrater reliability of BR echogenicity [9]. Our study also shows that this method of BR echogenicity measurements is applicable and provides excellent intra- and interobserver agreement in Korean patients with PD.
The raphe nuclei are an extensive cluster of neurons in the midline of the brainstem. The neurons mainly release serotonin and project to other parts of brain. Projections take role in various functional systems, such in motor, somatosensory and limbic [10]. Especially, the strong association of the BR with mood disorders like depression has been investigated. The connection between nucleus raphe dorsalis in the midbrain and orbital cortex is considered as the contributing pathway [11,12]. Few studies about the correlation of TCS finding to signal alteration on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has been reported, suggesting that hypoechogenicity may reflect a structural disruption of mesencephalic fiber tracts of the dorsal RN. This interpretation would be in line with reported corresponding increased T2-relaxation time of BR in patients with unipolar depression suggesting a pathology affecting the serotonergic raphe nuclei. However, the anatomical image of the raphe nuclei cannot be consistently identified in MRI data [13]. Instead, reduced echogenicity of BR in TCS better indicates the reduction of the serotonergic neurotransmitter system. The precise pathophysiological and morphological interpretation of BR hypoechogenicity is still speculative. Further multimodal imaging studies on depressive patients with the combination of histopathology are needed to speculate the impact of the hypoechogenic BR in the pathophysiology of depression.
Two major limitations of TCS impede its more widespread use. First, it is highly operator dependent requiring detailed three-dimensional knowledge of brain anatomy and experience for accurate interpretation. Therefore, standardized scanning protocol with transducer positioning and orientation, depth selection, and structure identification will support good TCS research applications. Second, it is also hampered by the high rate of inadequate acoustic windows. In our study, a total of 49 (24.5%) patients had a bilateral poor TW, significantly more women than men. It is well known that a poor TW is common in oriental or black people, especially in elderly women, as observed in TCD study [14]. There were few studies regarding to the rate of poor TW in TCS study. TCS examination is performed through the transtemporal bone window using an ultrasound system equipped with a phased-array transducer (2.0-3.5 MHz). TCS modes were set at an image depth of 14-16 cm and a dynamic range of 45-60 dB. In TCD study, Doppler signals from the main stem of middle cerebral artery were obtained transtemporally with a traditional 2-MHz transducer at depths of 56-60 mm. Compared to other TCD studies, the poor TW rate in our patient sample is lower than that found in previous studies conducted in Asian populations, including a Korean study showing a poor TW rate of 34% [15-17].
In conclusion, altered echogenicity of the BR in TCS may support the pathogenic link between depression and PD [18,19]. Hypoechogenic BR is a correlate of central serotonergic dysfunction [19]. Using the current methods, we will conduct further studies regarding the BR and neuropsychiatric symptoms in Korean patients with PD.
Fig. 1.
Sonographic axial images of the brainstem raphe. The butterfly-shaped midbrain was encircled with a dotted line for better visualization. Arrowheads indicate the brainstem raphe (BR). Arrows indicate red nuclei, used as the reference echogenicity of the raphe nuclei. (A) Normal echogenicity (grade III), (B) hypoechogenic BR (grade II), (C) invisible BR (grade I).
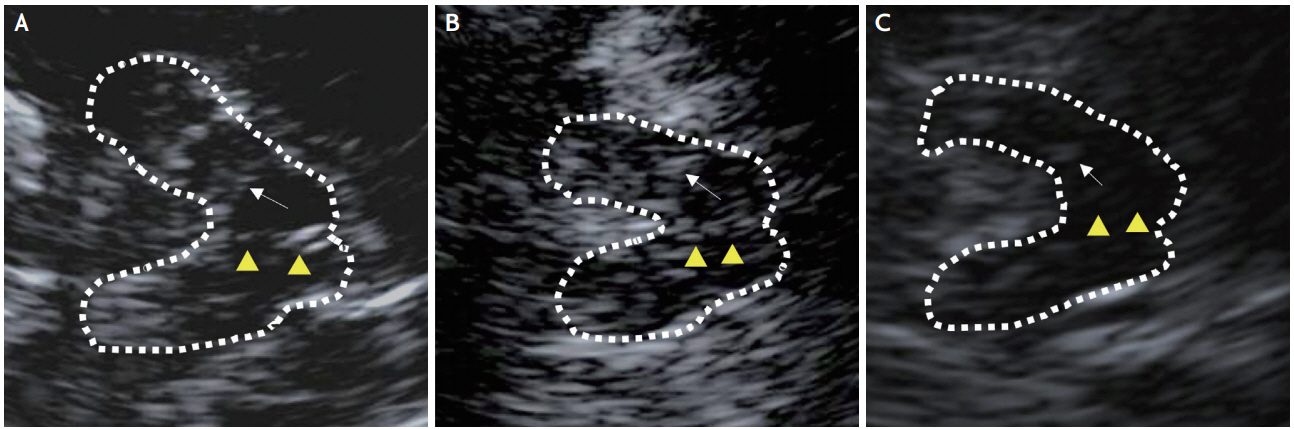
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of enrolled patients grouped by TW
Table 2.
Baseline characteristics of enrolled patients grouped by TW and sex
REFERENCES
1. Reijnders JS, Ehrt U, Weber WE, Aarsland D, Leentjens AF. A systematic review of prevalence studies of depression in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2008;23:183-189 quiz 313.


2. Ishihara L, Brayne C. A systematic review of depression and mental illness preceding Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol Scand. 2006;113:211-220.


3. Stanković I, Stefanova E, Žiropadja L, Mijajlović M, Pavlović A, Kostić VS. Transcranial midbrain sonography and depressive symptoms in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol. 2015;262:689-695.


4. Becker T, Becker G, Seufert J, Hofmann E, Lange KW, Naumann M, et al. Parkinson’s disease and depression: evidence for an alteration of the basal limbic system detected by transcranial sonography. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1997;63:590-596.



5. Krogias C, Walter U. Transcranial sonography findings in depression in association with psychiatric and neurologic diseases: a review. J Neuroimaging. 2016;26:257-263.


6. Cho JW, Baik JS, Lee MS. Mesencephalic midline change on transcranial sonography in early Parkinson’s disease patients with depression. J Neurol Sci. 2011;310:50-52.


7. Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1992;55:181-184.



8. Ghourchian S, Zamani B, Poorkosary K, Malakouti SK, Rohani M. Raphe nuclei echogenicity changes in major depression. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2014;28:9.


9. Walter U, Hoeppner J, Prudente-Morrissey L, Horowski S, Herpertz SC, Benecke R. Parkinson’s disease-like midbrain sonography abnormalities are frequent in depressive disorders. Brain. 2007;130(Pt 7):1799-1807.



10. Hornung JP. The human raphe nuclei and the serotonergic system. J Chem Neuroanat. 2003;26:331-343.


11. Peyron C, Petit JM, Rampon C, Jouvet M, Luppi PH. Forebrain afferents to the rat dorsal raphe nucleus demonstrated by retrograde and anterograde tracing methods. Neuroscience. 1998;82:443-468.


12. Michelsen KA, Prickaerts J, Steinbusch HW. The dorsal raphe nucleus and serotonin: implications for neuroplasticity linked to major depression and Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Brain Res. 2008;172:233-264.


13. Tiger M, Ruck C, Forsberg A, Varrone A, Lindefors N, Halldin C, et al. Reduced 5-HT(1B) receptor binding in the dorsal brain stem after cognitive behavioural therapy of major depressive disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2014;223:164-170.


14. Seidel G, Kaps M, Gerriets T. Potential and limitations of transcranial color-coded sonography in stroke patients. Stroke. 1995;26:2061-2066.


15. Lien LM, Chen WH, Chen JR, Chiu HC, Tsai YF, Choi WM, et al. Comparison of transcranial color-coded sonography and magnetic resonance angiography in acute ischemic stroke. J Neuroimaging. 2001;11:363-368.


16. Itoh T, Matsumoto M, Handa N, Maeda H, Hougaku H, Hashimoto H, et al. Rate of successful recording of blood flow signals in the middle cerebral artery using transcranial Doppler sonography. Stroke. 1993;24:1192-1195.


17. Kwon JH, Kim JS, Kang DW, Bae KS, Kwon SU. The thickness and texture of temporal bone in brain CT predict acoustic window failure of transcranial Doppler. J Neuroimaging. 2006;16:347-352.


-
METRICS

-
- 1 Crossref
- Scopus
- 3,951 View
- 53 Download
- Related articles in AC





